I’ve compiled a list of questions and answers about fundamental topics in Java that I believe every Java developer should be aware of. This is part 2, covering the topic of Constructors.
What is a Java constructor?
It's a special type of method that has the same name as the class it contains.
It's used to initialize an instance of a class.
How is a constructor used to initialize an object of a class?
To initialize an object, a constructor is called using the
newkeyword. Let's say we have a Person class, here's how we can create an object of this class: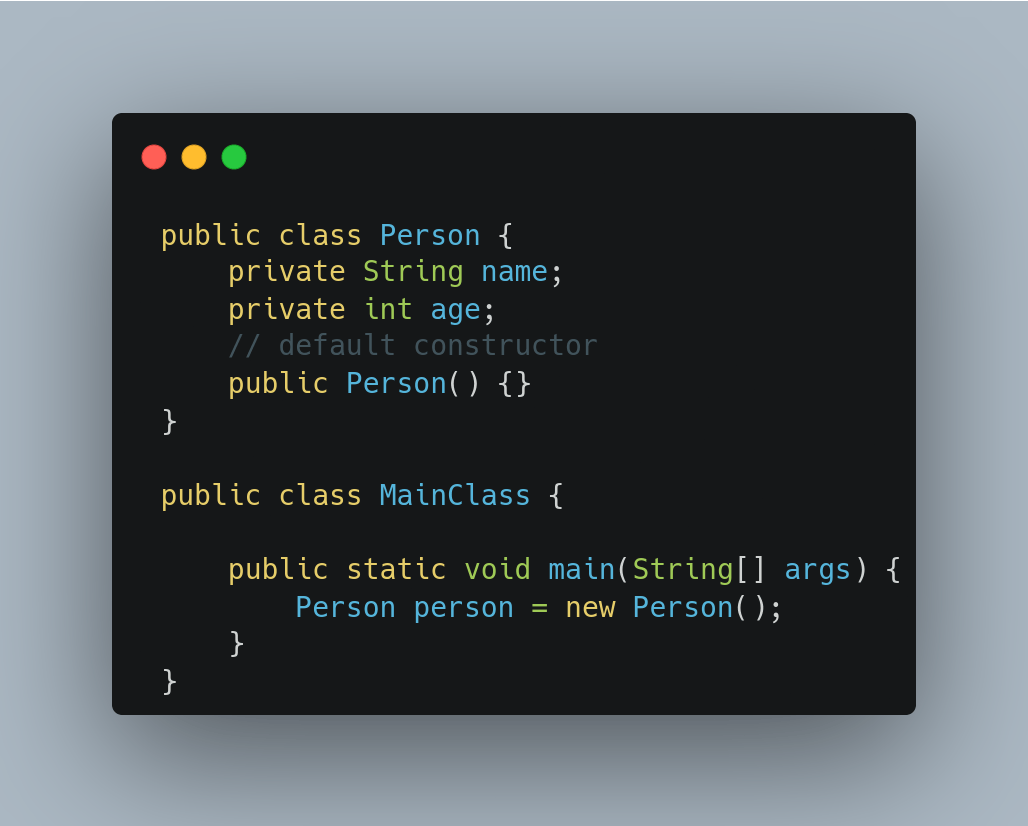
We created an object of Person class using the new keyword followed by the constructor Person()
What are the types of constructors in Java?
No-args constructor (default)
Can be explicitly defined or else a default one will be provided by Java compiler
Does not take any parameters. Hence called 'no-args'
The syntax is
ClassName() {}Can be used to create objects and initialize instance variables of a class with their default values:

Parameterized Constructor
Must be defined with one or more parameters
Used to create objects and initialize instance variables with customized values. Let's modify the above example to demonstrate how to create and use a parameterized constructor:
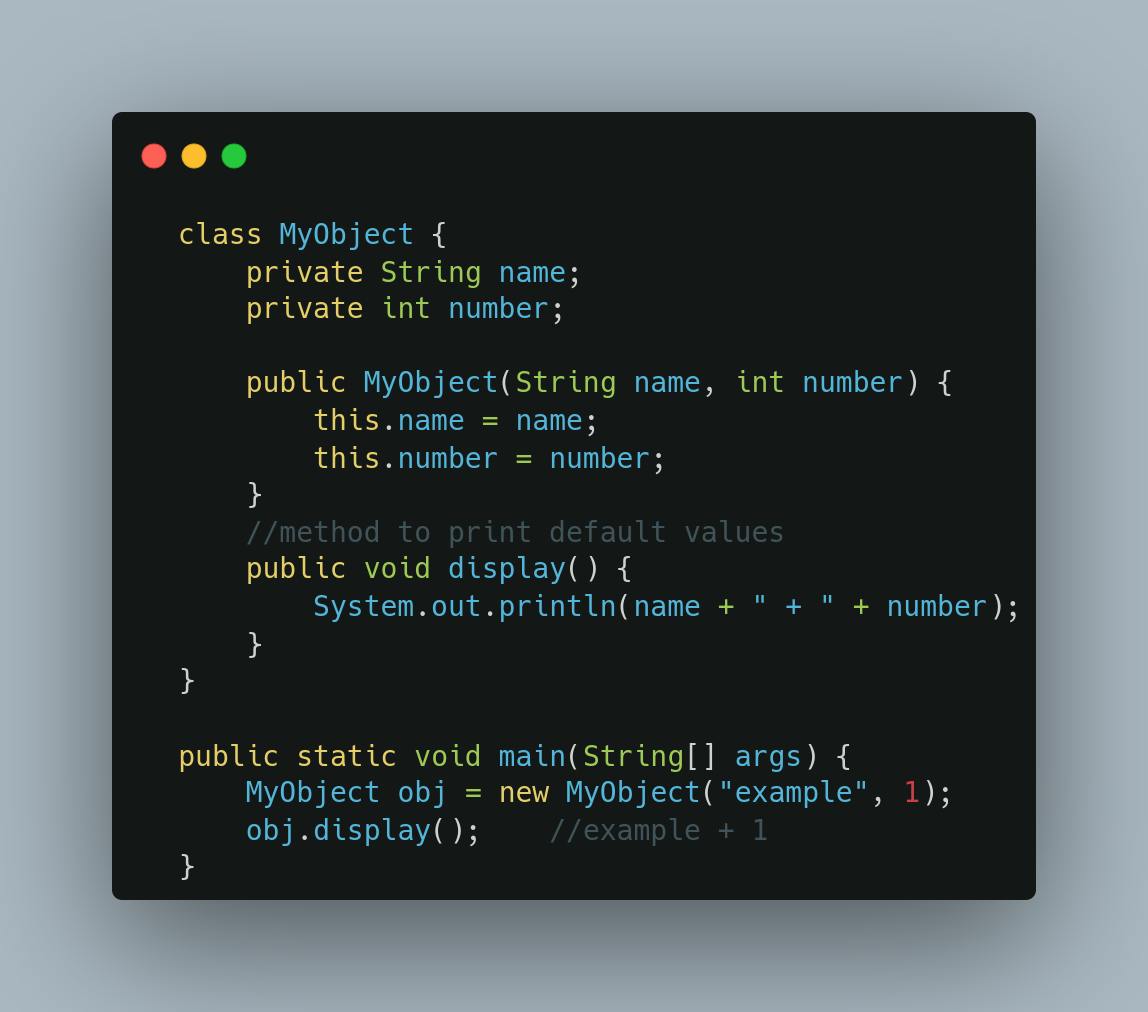
What are the rules for creating a Java constructor?
There are some rules such as:
Must have the same name as the class it's defined in
Must not have a return type, not even
voidIf not explicitly defined, a default no-args constructor is provided by Java compiler
Can have any access modifier like
public,private,protectedorpackagethat determines the level of access to the constructor from another classCan call another constructor using the keyword
this()Can call a superclass constructor from the subclass using keyword
super()provided that the call must be the first statement in the constructor
What's the difference between a constructor and a method?
There are some differences such as:
| Constructor | Method |
| Used to initialize objects | Used to perform a specific operation |
| Must have the same name as the class | Can be named anything |
| Does not have a return type | Always has a return type, including void |
| A default constructor is provided by Java compiler if not explicitly defined | No method is provided in any case |
What is Constructor chaining?
This concept refers to the process of invoking a constructor from another constructor within the same class or subclass. It's performed using the keyword this in the same class or super from the subclass, while making sure the call is the first statement inside the constructor. This is useful in reducing code duplication by reusing the initialization code that's already defined in one constructor.
Let's look at the code below:
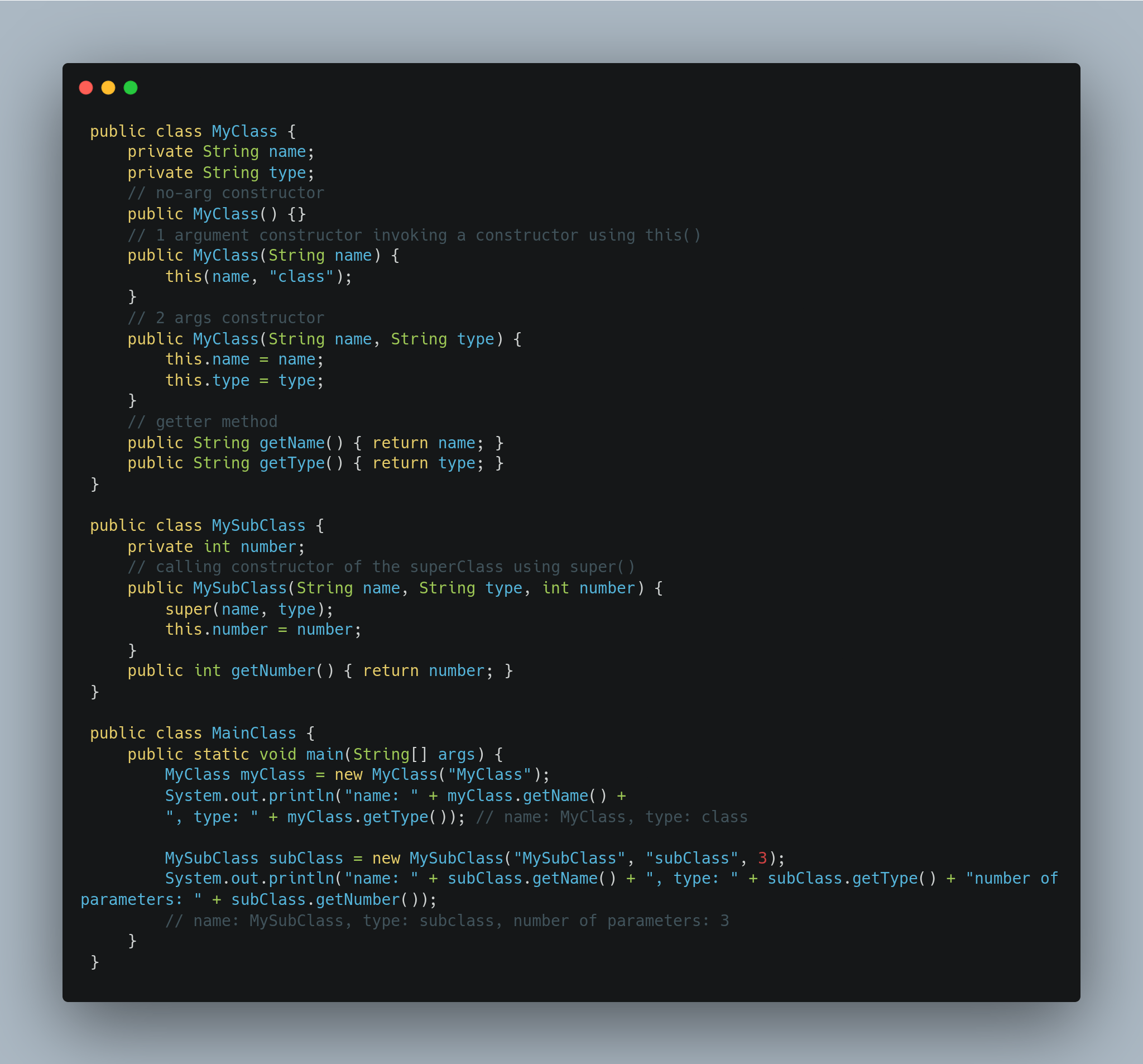
As you can see, we demonstrated two ways to perform constructor chaining:
MyClasshas three constructors: ano-argconstructor, a constructor with a single parameter that invokes another 3-parameter constructor and passes a default value in place of the type parameter.MySubClassclass extendsMyClassand defines a 3-args constructor which invokes a constructor from the subclass.
There you have it. This is part two of the series of Java questions and answers. I hope what we've discussed so far was helpful. Stay tuned for part two.

